 Chlamydia Infection: Symptoms, Treatments & Risk Factors
Chlamydia Infection: Symptoms, Treatments & Risk FactorsOral STDs: What are the symptoms? Sexually transmitted infections and diseases (STIs) are not contracted only through vaginal or anal sex, as any skin-to-dry contact with the genitals is sufficient to pass an STI to your partner. This means that oral sex using the mouth, lips or tongue may pose similar risks such as other sexual activities. The only way to reduce the risk of transmission is to use a barrier method or another for each sexual encounter. Continue reading to find out what sexually transmitted infections can spread through oral sex, symptoms to look for and how to test. - is caused by the bacterium Chlamydia trachomatis. It is the most common bacterial STI in the United States among all age groups. Chlamydia through oral sex, but it is more likely to be transmitted through anal or vaginal sex. Chlamydia may affect the throat, genitals, urinary tract and rectum. Most of the chlamydia that affects the throat does not cause symptoms. When symptoms appear, they may include a sore throat. Chlamydia is not a condition for life, and can be cured with the right. is a common STI caused by the bacteria Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The CDC estimates that each year they occur around gonorrhea, affecting people aged 15 to 24. Both gonorrhea and chlamydia can technically pass through oral sex according to CDC, but the exact risks. Those who engage in oral sex can also participate in vaginal or anal sex, so the cause of the condition may not be clear. Gonorrhea can affect the throat, genitals, urinary tract and rectum. Like chlamydia, the gonorrhea of the throat often shows no symptoms. When symptoms appear, it is usually a week after exposure and may include a sore throat. Gonorrhea can be cured with the right. However, there has been an increase in drug-resistant gonorrhea reports in the United States and around the world. CDC recommends that you repeat if your symptoms do not go away after you have completed the full course of antibiotics. It is also important for any partner to undergo tests and treatment for any STI that may have been exposed to. is a STI caused by the bacteria Treponema pallidum. It is not as common as other sexually transmitted infections. According to the , there were 115.045 new syphilis diagnoses in 2018. Syphilis can affect the mouth, lips, genitals, anus and rectum. If not treated, syphilis can also be extended to affect other parts of the body, including blood vessels and the nervous system. Syphilis symptoms occur in stages. The first stage (primary syphilis) is characterized by an indolorous sore (called chancre) in the genitals, straight or in the mouth. The sore can go unnoticed and will disappear on its own even without treatment. In the second stage (second stage), you can experience a skin rash, swollen lymph nodes and fever. The latent stage of the condition, which can last for years, shows no signs or symptoms. The third stage of the condition (tercial syphilis) can affect your brain, nerves, eyes, heart, blood vessels, liver, bones, and joints. It can also spread to a fetus during pregnancy and cause childbirth or other serious complications for the baby. Syphilis can be cured with appropriate antibiotics. If not treated, the condition will remain in the body and can cause serious health problems, such as organ damage and significant neurological results. Type 1 (HSV-1) is one of two types of common viral STI. HSV-1 is propagated mainly through oral-oral or oral-a-genital contact, causing oral herpes and genital herpes. According to the , HSV-1 affects approximately 3.7 billion people under the age of 50 worldwide. HSV-1 can affect the lips, mouth, throat, genitals, rectum and anus. Symptoms of oral herpes include blisters or sores (also called ) in the mouth, lips and throat. This is a lifelong condition that can spread even when symptoms are not present. Treatment can reduce or prevent herpes outbreaks and shorten their frequency. HSV-2 is transmitted mainly through sexual intercourse, causing genital herpes or anal. According to the , HSV-2 affects approximately 491 million people aged 15-49 worldwide. HSV-2 may spread through oral sex and, together with HSV-1 may cause serious illnesses like in some people, but this is rare. Symptoms of herpes esophagitis include: This is a lifelong condition that can spread even when you have no symptoms. Treatment can shorten and reduce or prevent herpes outbreaks. is the most common STI in the United States. The CDC estimates that they currently live with HPV. The virus can spread through oral sex as often as vaginal or anal sex does. HPV affects the mouth, throat, genitals, cervix, anus and rectum. In some cases, HPV will not show any symptoms. Certain types of HPV can cause laryngeal or respiratory papilomatosis, which affects the mouth and throat. Symptoms include: Several other types of HPV that affect the mouth and throat do not cause warts, but may cause head or neck cancer. HPV does not have a cure, but most HPV transmissions are cleaned by the body alone without causing problems. The warts of the mouth and throat may be removed by surgery or other treatments, but may also repeat with treatment. In 2006, FDA adopted a vaccine for children and young adults aged 11 to 26 to prevent the transmission of the most common high-risk strains. These are strains associated with cervical, anal, and head and neck cancers. It also protects against common strains that cause genital warts. In 2018, the FDA for adults up to 45 years old. The CDC estimates that in the United States they lived in 2018. HIV spreads more commonly through vaginal and anal sex. According to , your risk of spreading or acquiring HIV through oral sex is extremely low. HIV is a life-long disease, and many do not see any symptoms for years. People living with HIV may initially have flu-like symptoms. There is no cure for HIV. However, people with HIV can live longer, healthier lives by taking and staying in . For , annual tests (at least) for chlamydia and gonorrhea for all sexually active women under 25 years and for all sexually active men who have sex with men (MSM). MSM should also be analyzed for syphilis at least annually. People with new or multiple sex partners, as well as pregnant women, should also have annual STD exams. CDC also recommends that all persons aged 13 to 64 be tested for HIV at least once in their lives. You can visit your doctor or health clinic to be tested for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections. Many clinics offer free or low-cost testing options. What you can expect from a test differs between each condition. Types of tests include: Although sexually transmitted infections spread more through sexual intercourse, it is still possible to acquire them during oral sex. Using a condom or other barrier method, correctly and each time, is the only way to reduce your risk and prevent transmission. You should be tested regularly if you are sexually active. The sooner you know your condition, the sooner you get treatment. Last medical review on November 1, 2020Read this following
Chlamydia in the throat: Causes, remedies and diagnosis Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that typically affects mucous membranes of the vagina, penis and anus. Sometimes, however, it can develop in those of the throat. Chlamydia may lead to a . But if it only affects this area, it may not cause any symptoms at all. In some people, the infection develops both in the throat and in the genitals. Then learn more about the throat and available treatments. chlamydia in the throat does not cause symptoms. Other times, the infection causes redness and sore throat or mouth. Even if a person has no symptoms, the infection may happen. This is also true when chlamydia affects genitals. Chlamydia can, for example, pass from genitals to genitals or another person's throat. The infection most affects the genitals, where it can cause the following symptoms: If symptoms occur, they often start after the initial infection. Chlamydia is a bacterial infection. A person can develop it through genital contact, sharing sex toys, and—through contact with liquids, such as semen, of a person who has the infection. However, oral sex is a way to develop the infection because bacteria prefer mucous membranes of the vagina, anus or penis to those of the throat. A person cannot contract chlamydia through: While chlamydia is one of the most bacterial in the United States, the chlamydia of the throat is rare. A person can develop it with the penis of a person with chlamydia. It is also possible to develop it in the genitals through oral contact of a person with chlamydia in his or her throat. A person may not be aware that he has the infection because chlamydia does not always cause symptoms. For this reason, the use of barrier protection is important. The recommend taking the following steps to prevent the spread of STIs through oral sex: While experts recommend regular tests, it is a particularly good idea to have a :Some groups can benefit from annual tests, :In the throat, a doctor will probably use a cotton hysop to get a sample of fluid. Then they usually send the sample to a laboratory, which will test for the bacteria. If the result is positive, the person should inform any recent sexual partner. for chlamydia typically involves an antibiotic course, which can last 1 or 7 days. A person taking a 1 day dose should avoid sexual contact for 7 days. A person taking a 7-day course may resume sexual activity after completing it. Since the risk of repeated infection is high, a person must be tested in about 3 months. Chlamydia in the throat is not common. Most of the time it passes from the penis to the throat, but it can also spread from oral contact with the vagina or anus. To prevent this and other sexually transmitted infections, use a barrier method, such as a condom or a dental dam, during all forms of sexual activity and have regular STI controls. A doctor may treat chlamydia with a short course of antibiotics, but there is a high risk of reinfection, so taking precautions is key. Last medical review on 17 August 2020Most recent newsRelated coverage
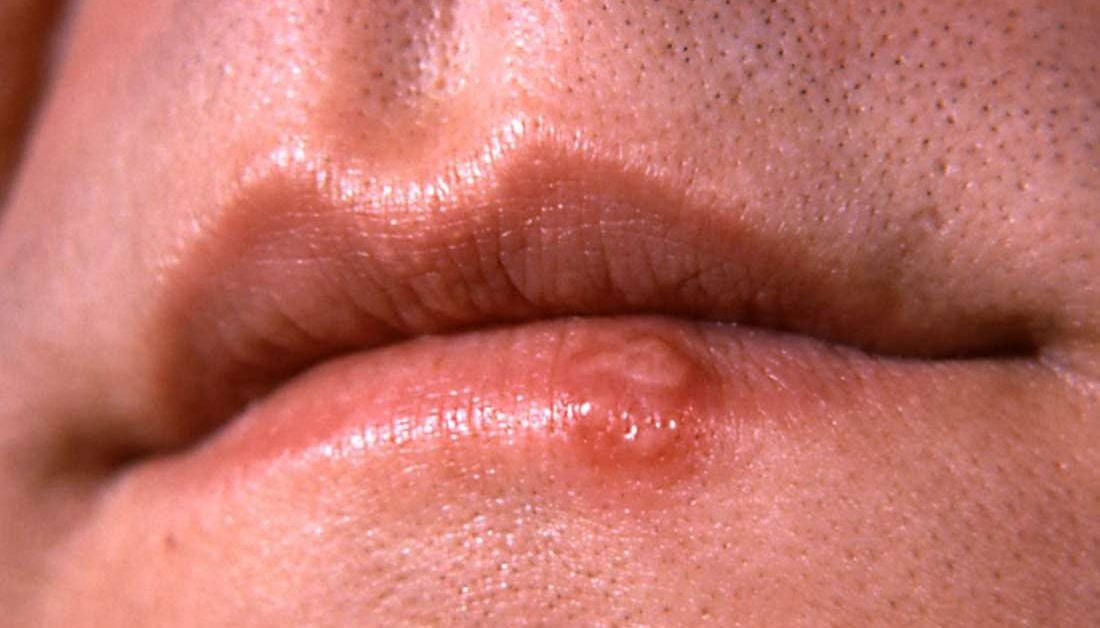
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Awareness: Types of Oral STDs - Embry Women's Health
Difference Between Chlamydia and Strep Throat | Difference Between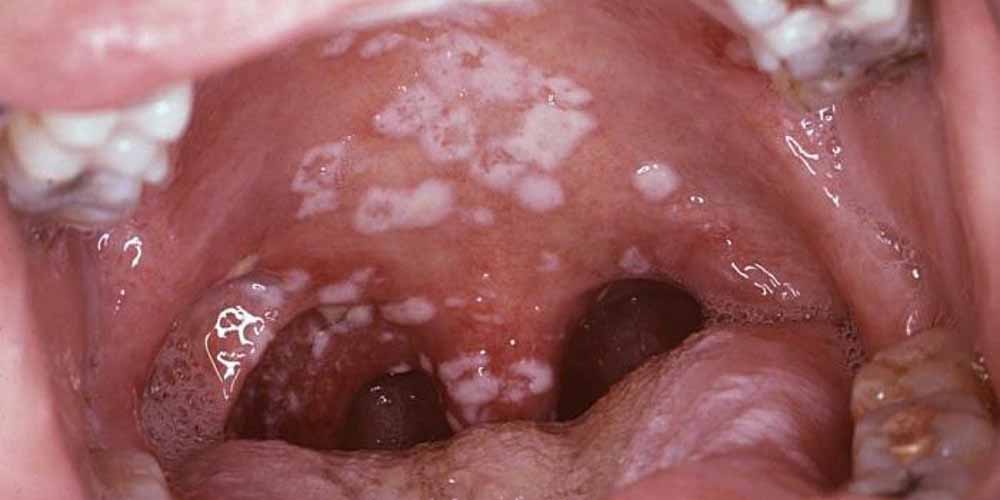
Chlamydia in the mouth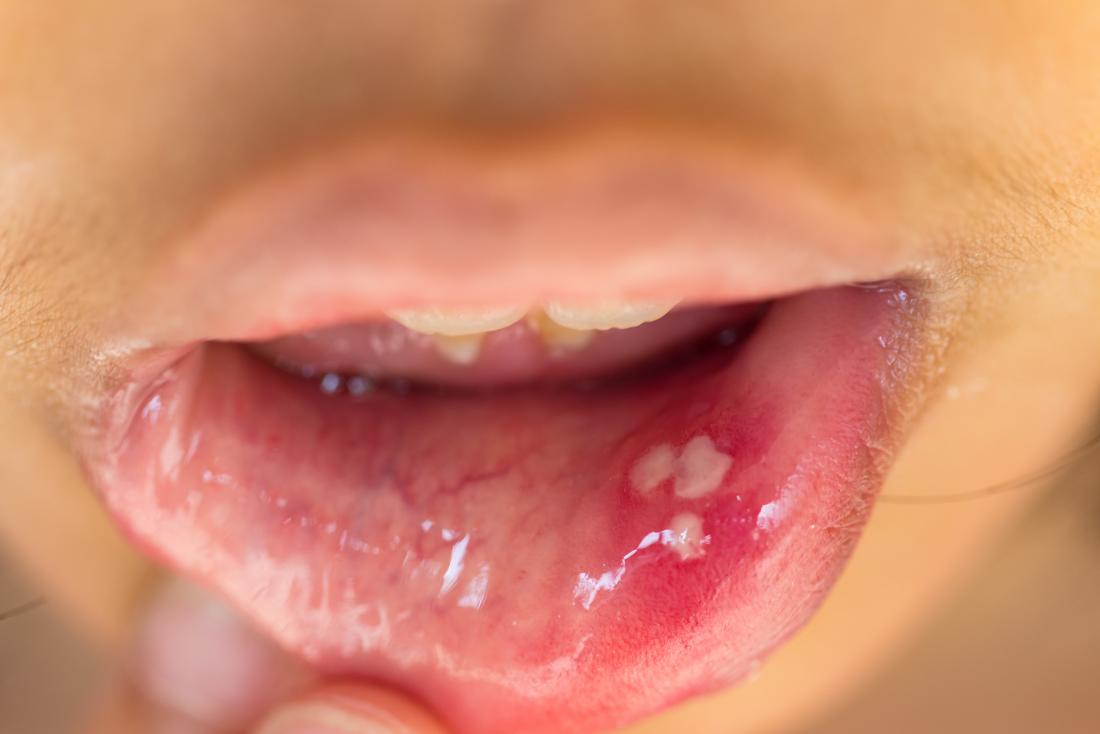
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
STDs and your oral health | Winning Smiles Dental Care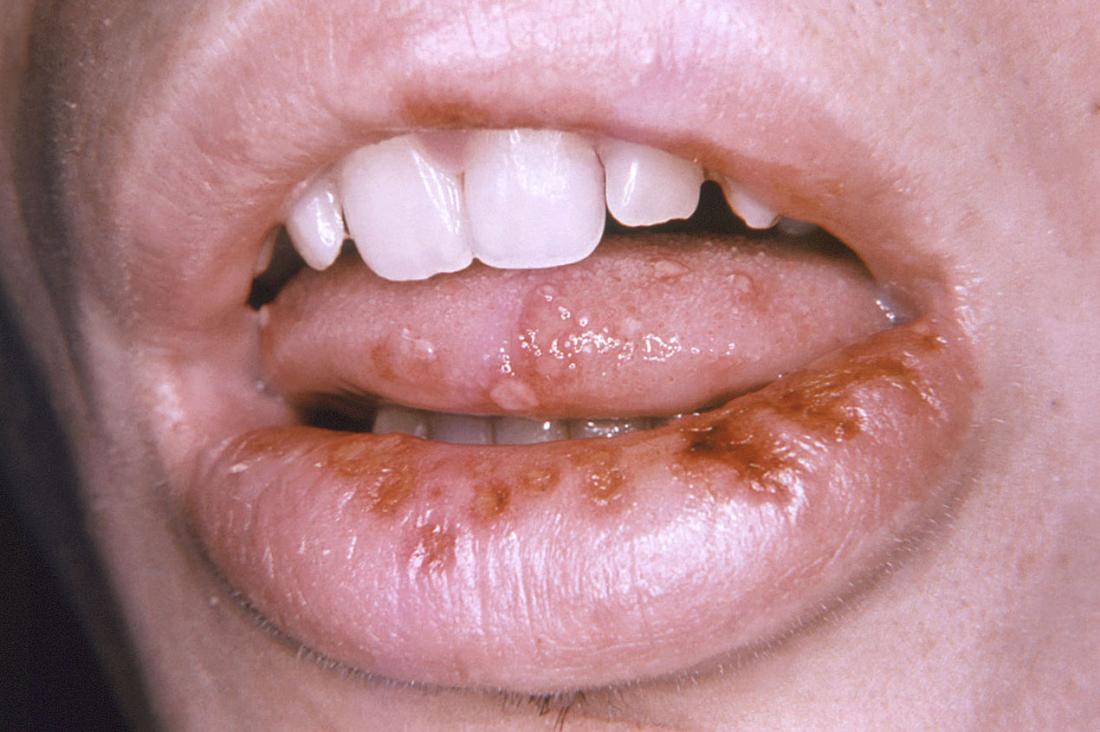
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Chlamydia Trachomatis (chlamydiatracho) - Profile | Pinterest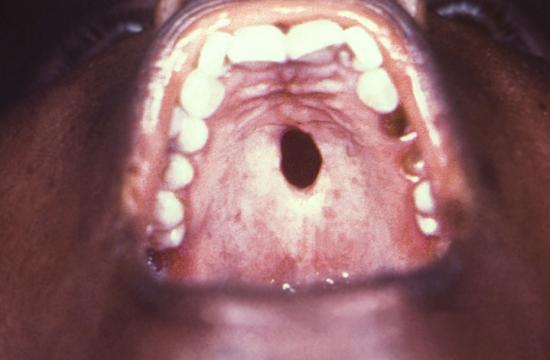
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Oral infections and systemic disease—an emerging problem in medicine - Clinical Microbiology and Infection
Difference Between Chlamydia and HPV | Difference Between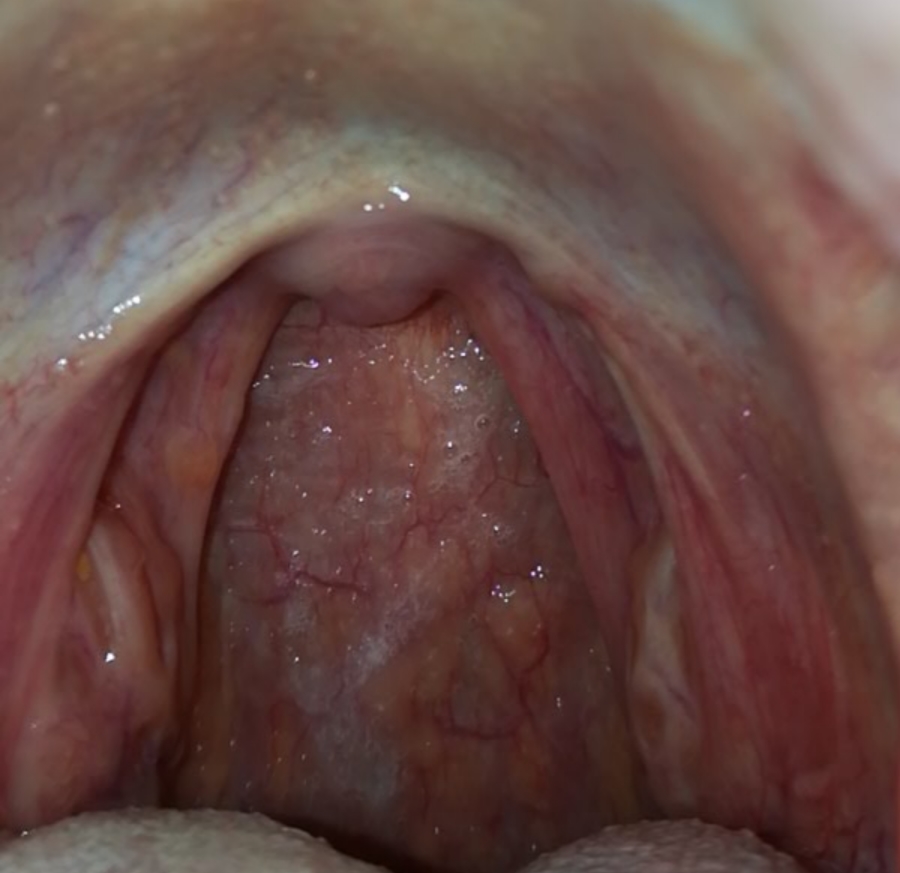
Oral HPV? or oral Chlamydia/Gonorrhoea? | Sexual Health | Forums | Patient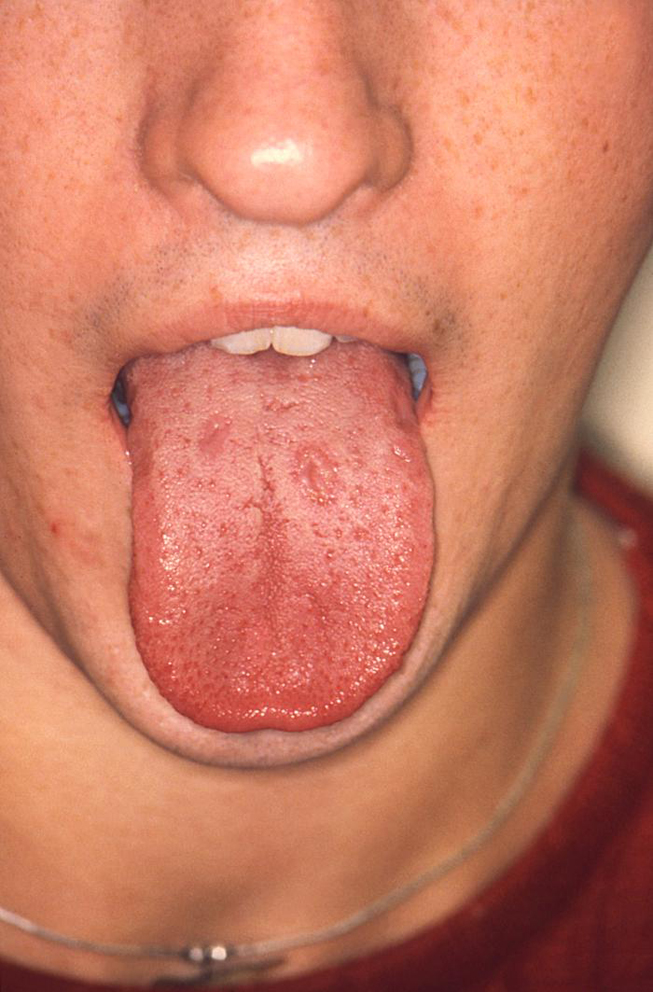
Course Content - #54071: Oral Manifestations of Sexually Transmitted Infections - NetCE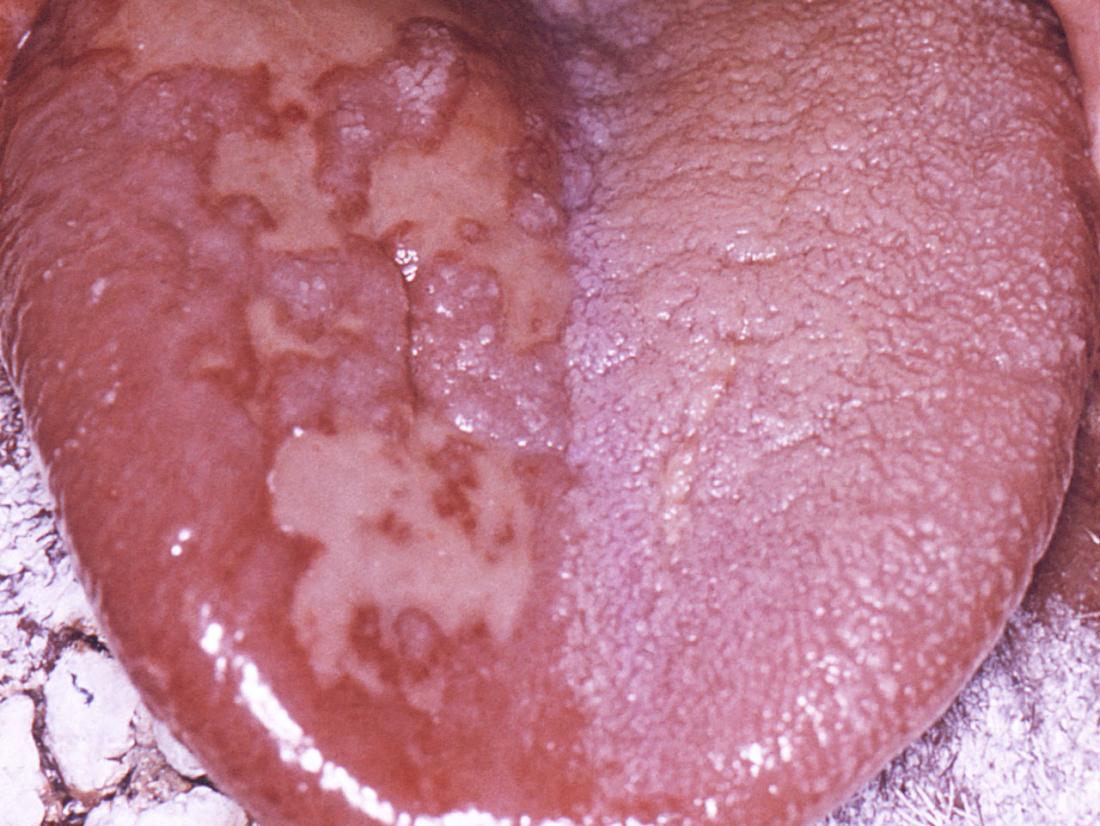
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Oral Yeast Infection (Oral Thrush) Symptoms, Causes & Treatment | epicuriousmorsels.com
chlamydia-in-mouth-oral-chlamydia-infection | Healthism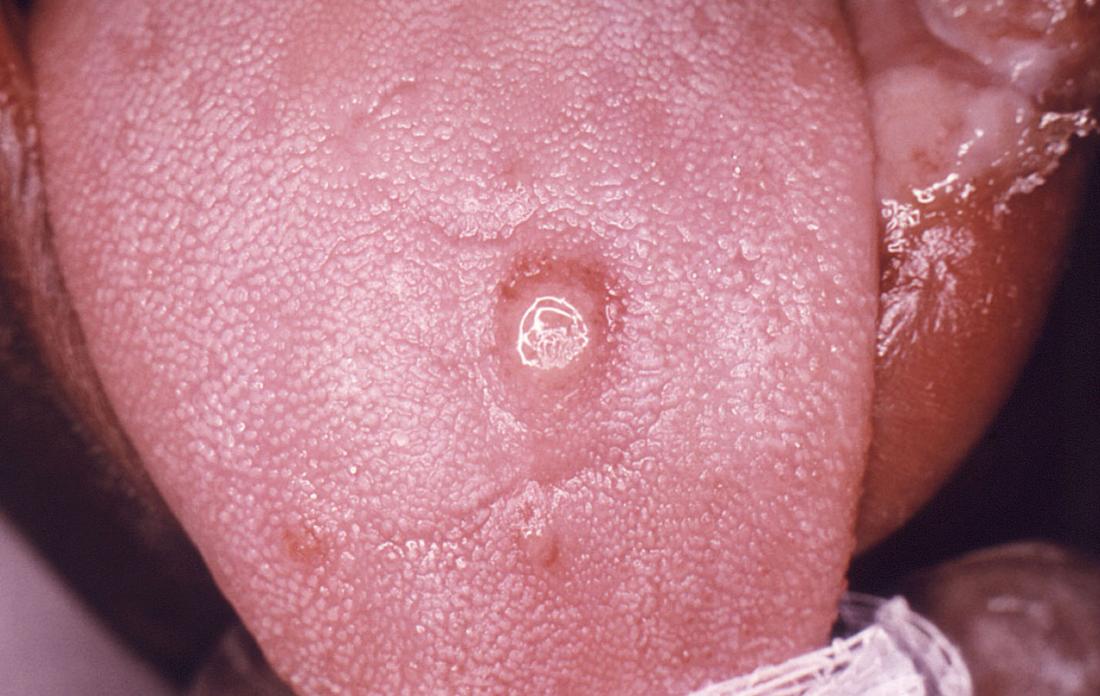
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Chlamydia Trachomatis (chlamydiatracho) - Profile | Pinterest
STD's by Estrella Parrilla
Oral STDs: Symptoms, Treatment, and More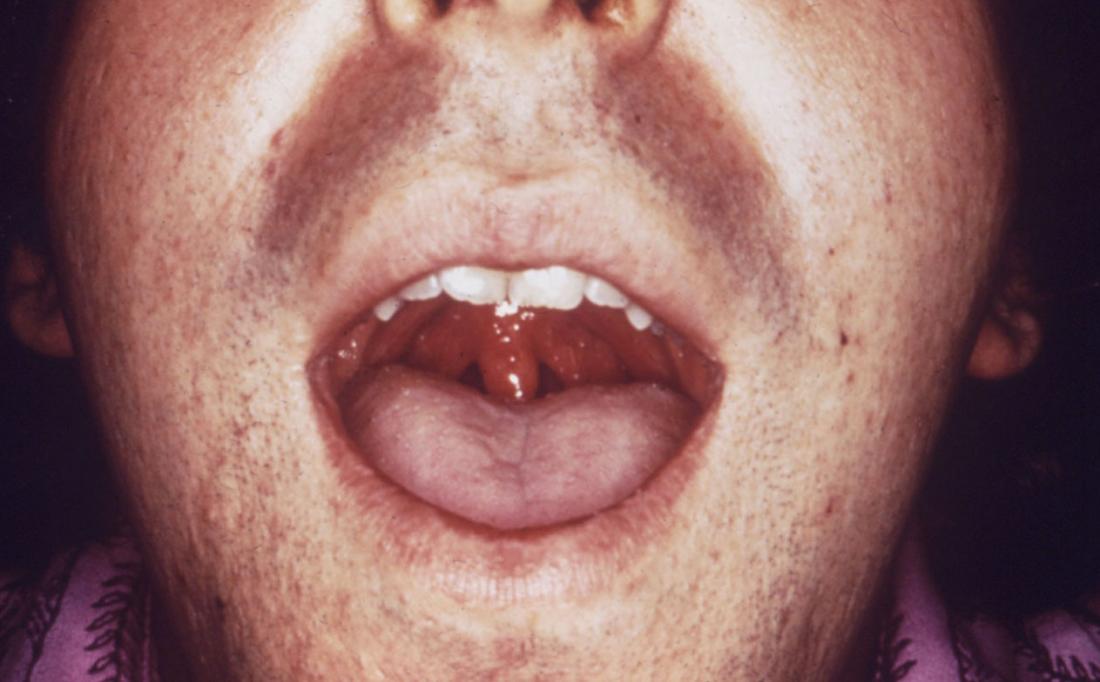
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Oral Chlamydia Treatment -
Oral Chlamydia Test in the U.S I Get At Home Test Kit Cost For $79 Only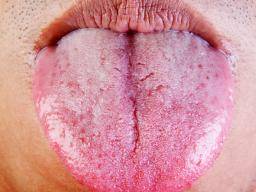
Chlamydia in throat: Pictures, symptoms, and treatments
Yes, you can get throat gonorrhea | Popular Science
FDA OKs First Chlamydia, Gonorrhea Tests for Throat, Rectal Swabs - POZ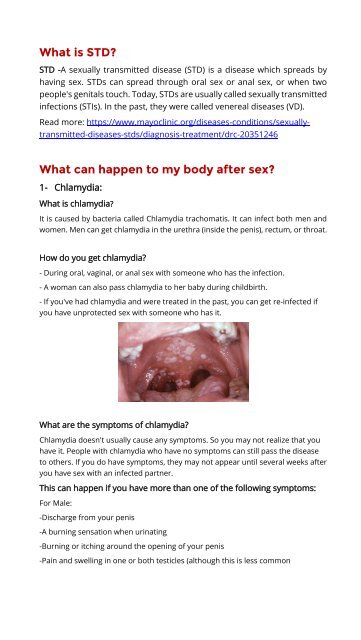
WhatsSex_STD
What To Do About Mouth Chlamydia | Superdrug Online Doctor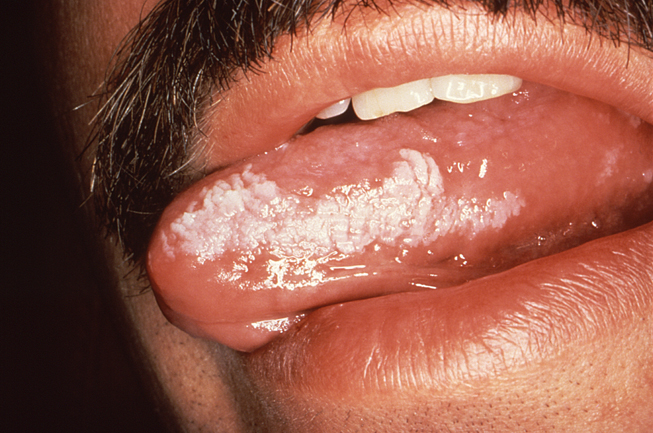
Course Content - #54071: Oral Manifestations of Sexually Transmitted Infections - NetCE
Oral STDs: Pictures, types, symptoms, treatment, and prevention
Oral Chlamydia Home Testing, Symptoms and Treatment | myLAB Box™
Chlamydia in the throat: causes, symptoms, and more - Blog | Everlywell: Home Health Testing Made Easy
Symtoms of The Most Common STI's - PDHPE ASSIGNMENT
Can You Get Chlamydia From Oral Sex? | myLAB Box™
Chlamydia in Throat: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, and More
Oral Chlamydia: Can it Affect the Mouth & Throat - STDcheck.com
How can you get an STI? More ways than you think | binx health
How is chlamydia transmitted? -
7 STDs You Can Catch From Oral Sex
Oral Chlamydia or Mouth Chlamydia: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment - YouTube
 Chlamydia Infection: Symptoms, Treatments & Risk Factors
Chlamydia Infection: Symptoms, Treatments & Risk Factors


































Posting Komentar untuk "what does chlamydia in the mouth look like"