Pitt Hopkins Like Syndrome
Pitt hopkins like syndrome. Pitt-Hopkins-Like Syndrome 1 Orrico et al. A number sign is used with this entry because Pitt-Hopkins-like syndrome-2 PTHSL2 is caused by compound heterozygous mutation in the NRXN1 gene 600565 on chromosome 2p16. 2009 reported an 18-year-old girl with a mental retardation syndrome resembling Pitt-Hopkins syndrome PTHS.
2001 described 2 sibs a brother and sister with severe mental retardation and multiple congenital anomalies including coarse facial features short stature seizures hypertrichosis short great toes and overbreathing. List of variants in gene NRXN1 reported as pathogenic for Pitt-Hopkins-like syndrome 2 Minimum submission review status. They may attend a special school or be in a class for children with disabilities.
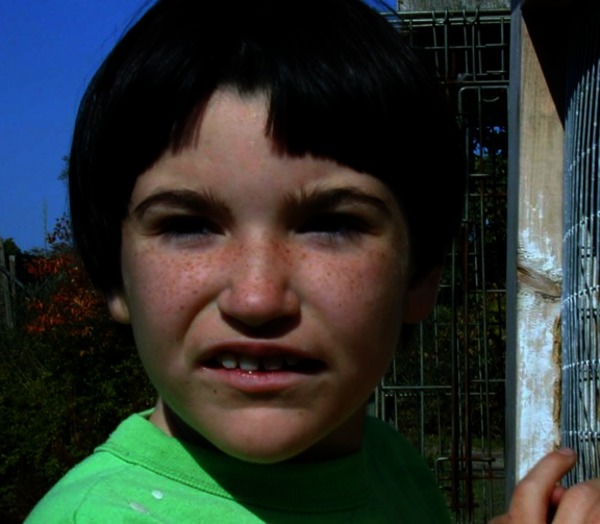
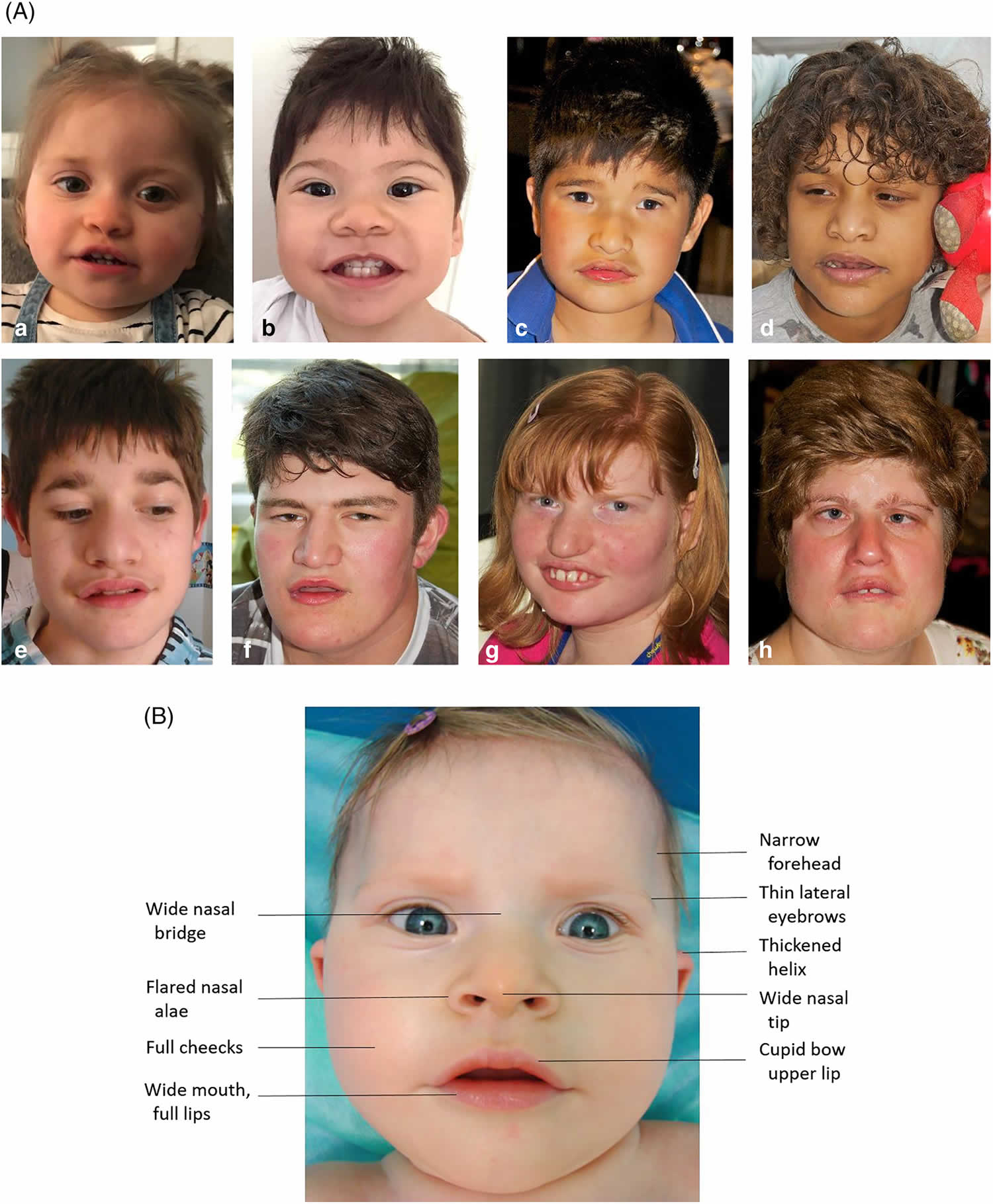
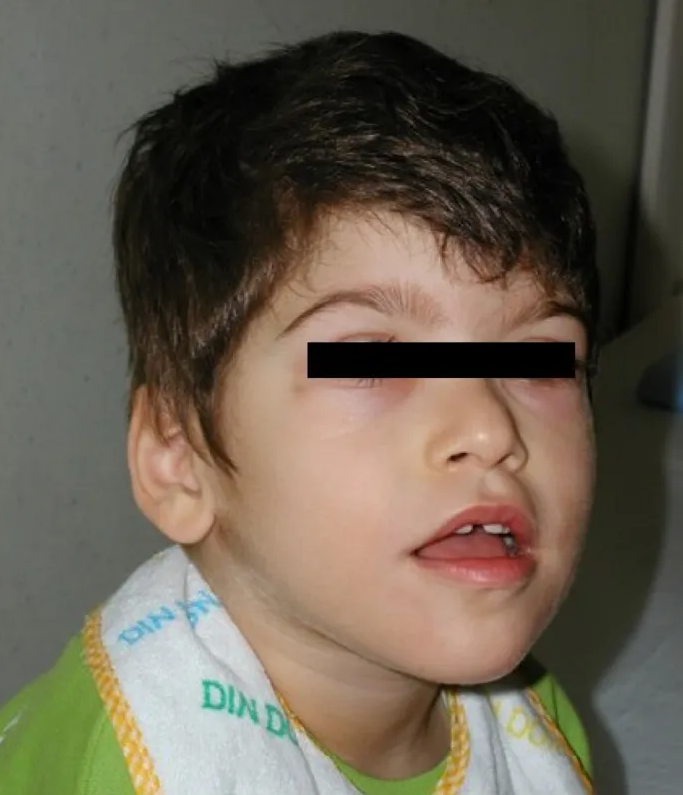
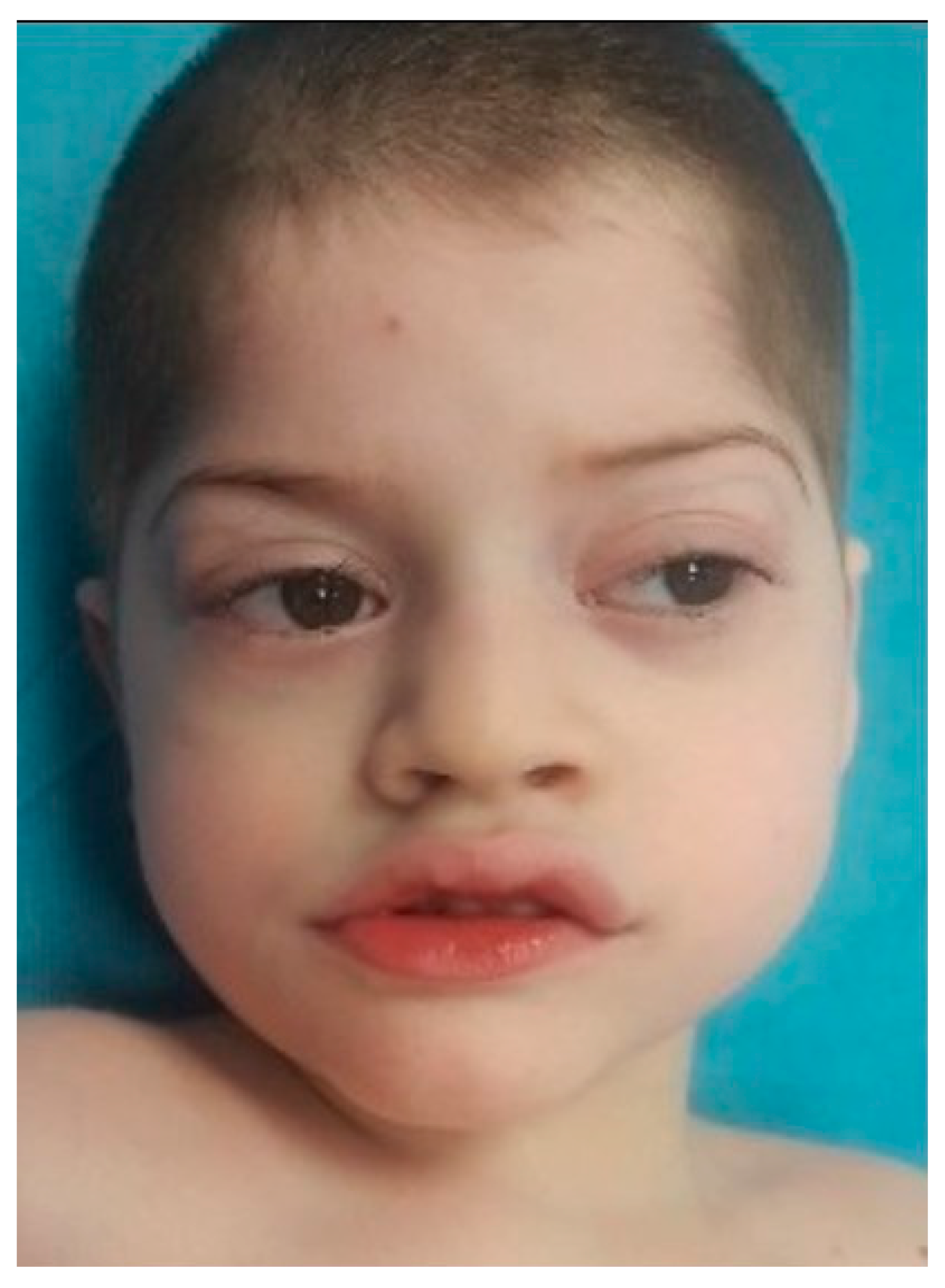
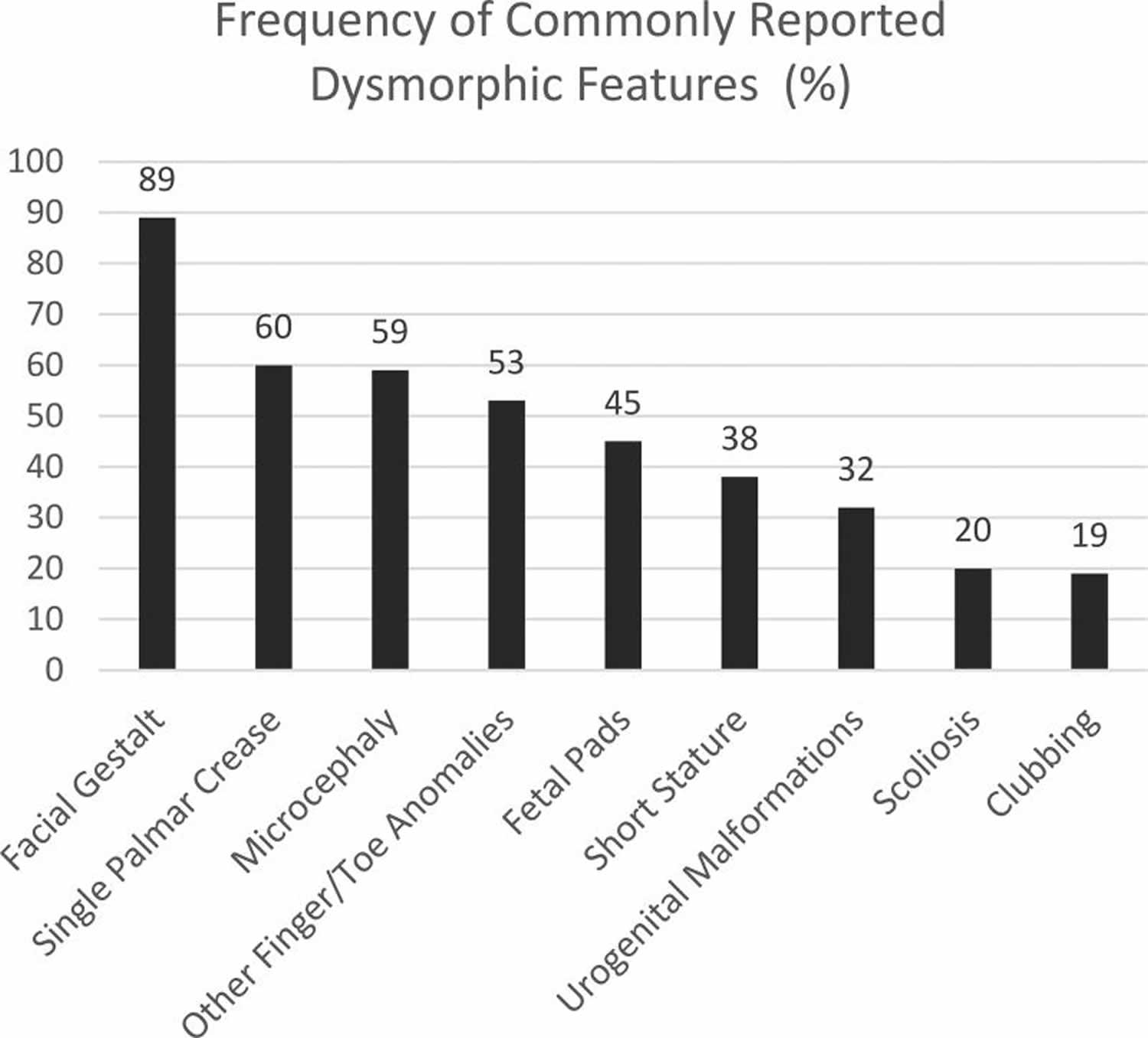
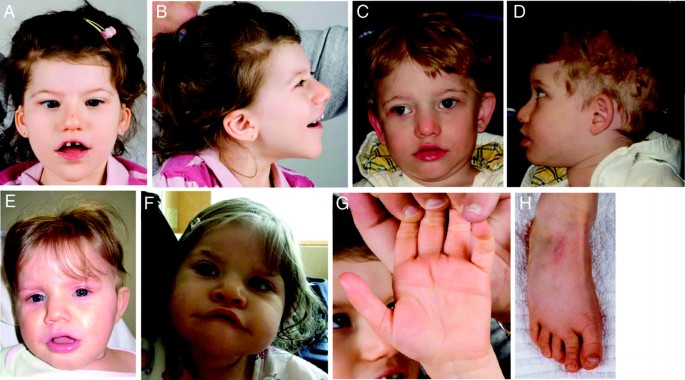
65 rows Pitt-Hopkins-like syndrome is a rare genetic syndromic intellectual disability disorder characterized by severe intellectual disability lack of speech with normal or mildly delayed motor development episodic breathing abnormalities early-onset seizures and facial dysmorphism which only includes a wide mouth. Explore symptoms inheritance genetics of. A condition in which epileptiform abnormalities are believed to contribute to the progressive disturbance in cerebral function.
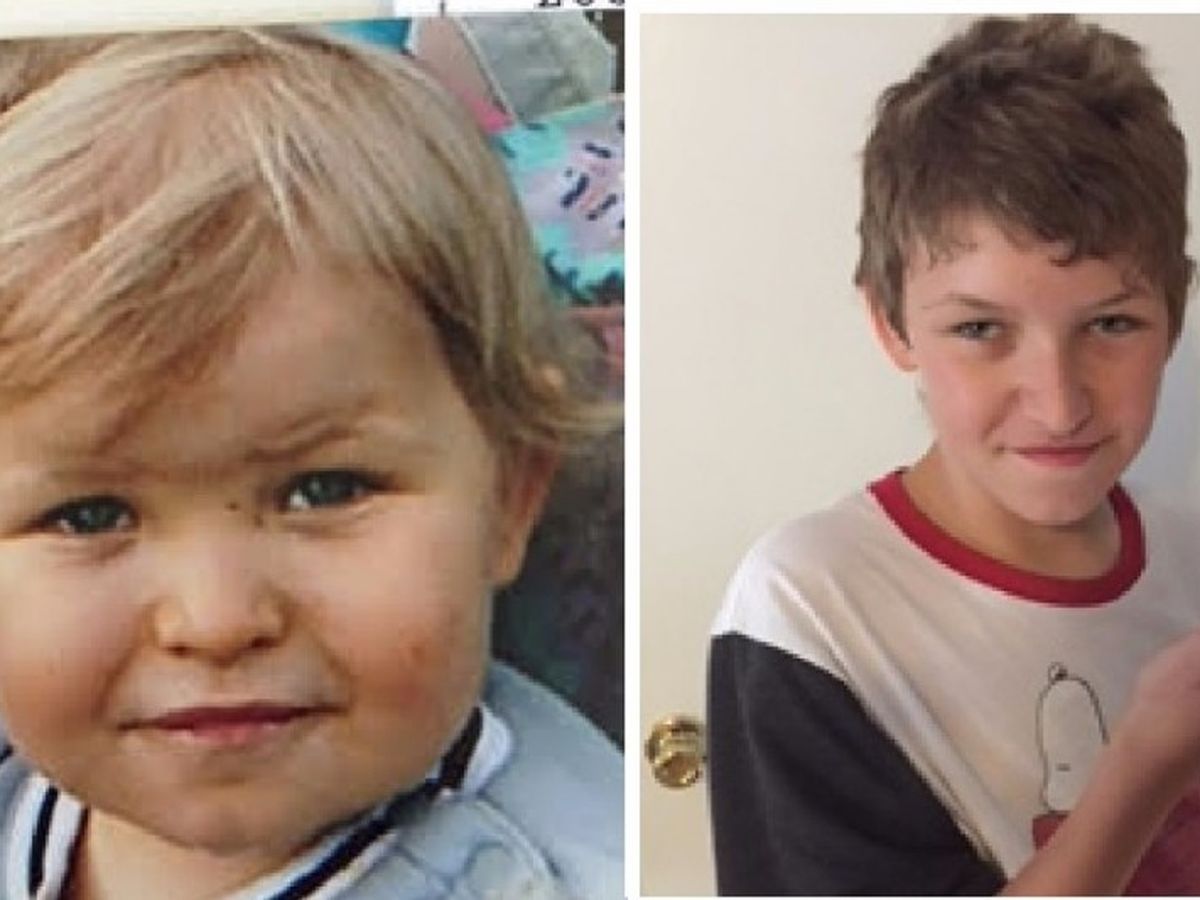
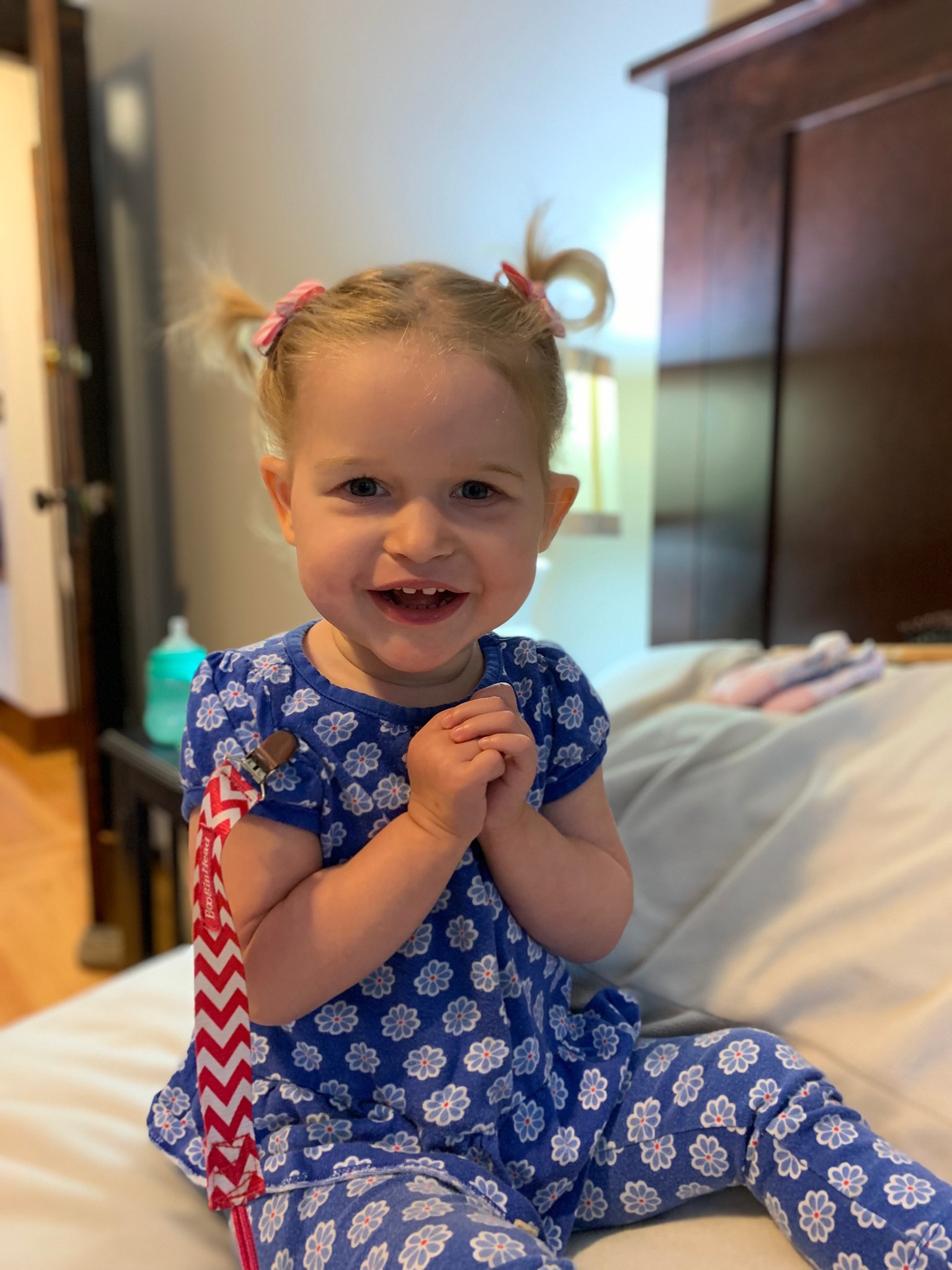
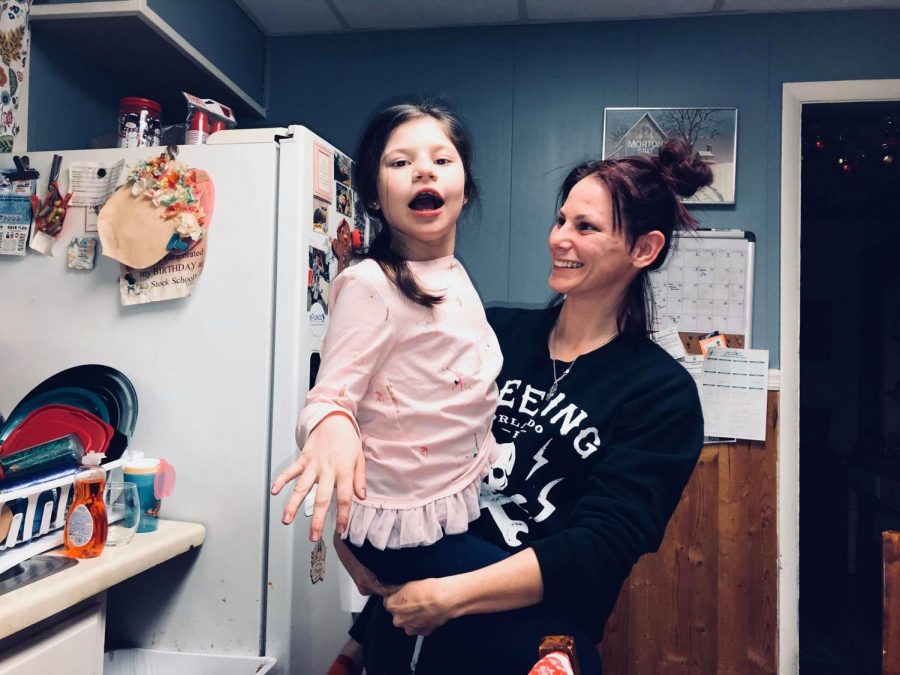
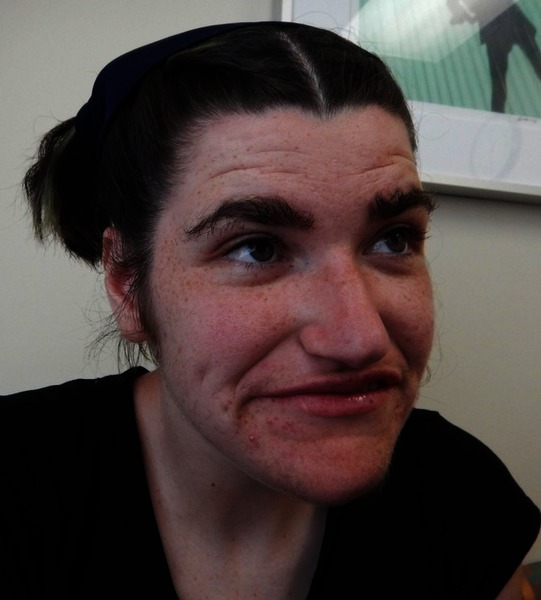
Pitt-Hopkins-like syndrome-2 is caused by mutation in the NRXN1 gene on chromosome 2p163. A rare genetic epilepsy characterized by relatively large head circumference or macrocephaly diminished or absent deep-tendon reflexes and mild gross motor delay in infancy followed by intractable focal seizures with language regression behavioral abnormalities hyperactivity attention deficit aggressiveautoaggressive behavior autistic features and intellectual disability later in life. Affected children have distinctive facial features and experience intellectual disability delays in reaching developmental milestones impaired ability to speak and can have recurrent seizures and breathing pattern abnormalities.
Pitt-Hopkins syndrome PTHS is a rare genetic neurological disorder. A new case of Pitt-Hopkins-like syndrome 2. However they share many of the same issues such as global developmental delay seizures lack of speech breathing irregularities and autistic features.
Criteria provided reviewed by. Article in En Spanish Authors F Ruiz-Botero 1 E Gómez-Pineda 2 H Pachajoa 3 Affiliations 1 Centro de Investigación en Anomalías Congénitas y Enfermedades Raras Facultad de Ciencias de la Salud. Children with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome PTHS can attend school.
Children and adults affected by these mutations are said to have Pitt Hopkins-like syndrome-1. Because they may need special accommodations in school they may eligible for an individual education plan IEP or a 504 plan.
Children with PTHS may need special accommodations.
A rare genetic epilepsy characterized by relatively large head circumference or macrocephaly diminished or absent deep-tendon reflexes and mild gross motor delay in infancy followed by intractable focal seizures with language regression behavioral abnormalities hyperactivity attention deficit aggressiveautoaggressive behavior autistic features and intellectual disability later in life. Pitt-Hopkins syndrome is a condition characterized by intellectual disability and developmental delay breathing problems recurrent seizures epilepsy and distinctive facial featuresPeople with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome have moderate to severe intellectual disability. Because they may need special accommodations in school they may eligible for an individual education plan IEP or a 504 plan. Epub 2017 Mar 23. Children with PTHS may need special accommodations. A syndrome characterized by severe mental retardation and variable additional symptoms such as impaired speech development autistic behavior breathing anomalies and a broad mouth resembling Pitt-Hopkins syndrome. These children and adults may have impaired speech development autistic behavior breathing anomalies constipation and strabismus resembling Pitt Hopkins syndrome. Criteria provided reviewed by. A condition in which epileptiform abnormalities are believed to contribute to the progressive disturbance in cerebral function.
A rare genetic epilepsy characterized by relatively large head circumference or macrocephaly diminished or absent deep-tendon reflexes and mild gross motor delay in infancy followed by intractable focal seizures with language regression behavioral abnormalities hyperactivity attention deficit aggressiveautoaggressive behavior autistic features and intellectual disability later in life. Criteria provided reviewed by. However they share many of the same issues such as global developmental delay seizures lack of speech breathing irregularities and autistic features. These children and adults may have impaired speech development autistic behavior breathing anomalies constipation and strabismus resembling Pitt Hopkins syndrome. Children with Pitt-Hopkins syndrome PTHS can attend school. Pitt-Hopkins-Like Syndrome 1 Orrico et al. Pitt-Hopkins syndrome PTHS is a rare genetic neurological disorder.



































Posting Komentar untuk "Pitt Hopkins Like Syndrome"